L Type, LL Type, KL Type, Embedded (G), Extruded Finned Tubes
- OD: 16 – 219mm
- WT: 1 – 8mm
- Length: 1000 – 33000mm
- Base Tubes: ASTM A179, A192, EN 10216-2 P235GH/P265GH TC1/TC2, DIN 17175 St35.8, St45.8
L Type, LL Type, KL Type, Embedded (G), Extruded Finned Tubes
Finned tubes, including L Type, LL Type, KL Type, Embedded (G), and Extruded varieties, are crucial components in heat exchangers, widely utilized across industries such as power generation, petrochemicals, and HVAC systems. Each type of finned tube is engineered to enhance heat transfer efficiency and withstand specific operational demands, from moderate thermal requirements to high-temperature, high-pressure environments. The design variations—ranging from the simple, cost-effective L Type to the robust, corrosion-resistant Extruded fins—make these tubes indispensable in optimizing energy efficiency, improving system performance, and extending the lifespan of heat exchangers in diverse industrial applications.
‘L’ FINNED TUBE
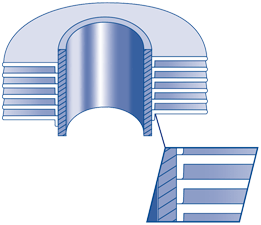
The strip material is subjected to controlled deformation under tension, giving the optimum contact pressure of the foot of the fin onto the base tube, thus maximizing the heat transfer properties.
The foot of the fin considerably enhances the corrosion protection of the base tube.
- Maximum working temperature: 150°c
- Atmospheric corrosion resistance: medium
- Mechanical resistance resistance: low
- Fin materials: aluminum, copper
- Tube materials: any theoretical limit
‘LL’ FINNED TUBE
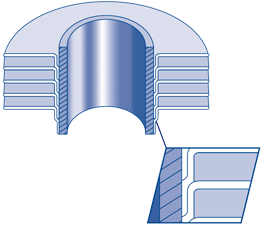
It is manufactured the same way as the ‘L’ finned tube type, except that the fin foot is overlapped to completely enclose the base tube, thereby giving excellent corrosion resistance. This finned tube is often used as an alternative to the more expensive extruded type fin in corrosive environments.
- Maximum working temperature: 180°c
- Atmospheric corrosion resistance: high
- Mechanical resistance: low
- Fin materials: aluminum, copper
- Tube materials: any theoretical limit
‘KL’ FINNED TUBE
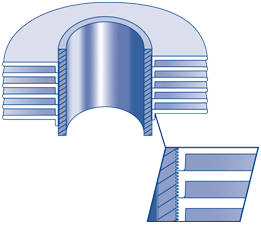
It is manufactured exactly as the ‘L’ finned tube except that the base tube is knurled before the fin foot is applied. After application, the fin foot is knurled into the corresponding knurling on the base tube, enhancing the bond between the fin and tube and improving heat transfer characteristics.
- Maximum working temperature: 260°c
- Atmospheric corrosion resistance: medium
- Mechanical resistance: medium
- Fin materials: aluminum, copper
- Tube materials: any theoretical limit
‘G’ EMBEDDED FINNED TUBE
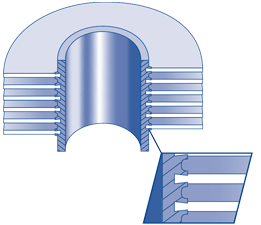
The fin strip is wound into a machined groove and securely locked into place by backfilling with base tube material. This ensures that maximum heat transfer is maintained at high tube metal temperatures.
- Maximum working temperature: 400°c
- Atmospheric corrosion resistance: low
- Mechanical resistance: medium
- Fin materials: aluminum, copper, carbon steel
- Tube materials: any theoretical limit
EXTRUDED FINNED TUBE
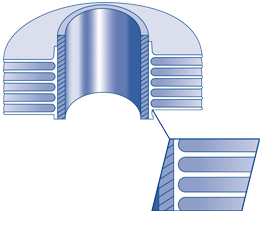
This fin type is formed from a bimetallic tube consisting of an aluminum outer tube and an inner tube of almost any material. The fin is formed by rolling material from the outside of the exterior tube to give an integral fin with excellent heat transfer properties and longevity. The extruded fin offers outstanding corrosion protection for the base tube.
- Maximum working temperature: 285°c
- Atmospheric corrosion resistance: high
- Mechanical resistance: high
- Fin materials: aluminum
- Tube materials: any theoretical limit
Specifications of Finned Tubes
| Product Name | L Type, LL Type, KL Type, Embedded (G), Extruded Finned Tubes |
| Base Tube | ASTM A179, A192, EN 10216-2 P235GH/P265GH TC1/TC2, DIN 17175 St35.8, St45.8 |
| Outer Diameter | 16 – 219 mm |
| Wall Thickness | 1 – 8 mm |
| Length | 1000 – 33000m |
| Fin Materials | Copper-Nickel, Copper, AA1050, AA1060, AA1080, AA1100 |
| Fin Height Range | 6 – 30mm |
| Fin Thickness Range | 0.2-0.6mm |
| No. of Fins per Inch/Fin Pitch | 8 – 16 FPI |
| No. of Fins per Meter/Fin Pitch | 250 – 500 FPM |
| Shape of Tubes | Straight Tube, U-Tube. |
| Packing Details | Tube ends are covered with plastic caps and packed in wooden or steel frame boxes. |
| Place of Origin | Made in China |
| MOQ | 3 Tons/Size |
| inspection Certificate | EN 10204:2005 Type 3.1, EN 10204:2005 Type 3.2 by SGS, BV, TUV |
| Transportation | Railway, By Sea |
Applications of L Type, LL Type, KL Type, Embedded (G), Extruded Finned Tubes
Finned tubes are essential components in heat exchangers used across various industries, including power generation, chemical processing, and HVAC systems. The different finned tubes, including L Type, LL Type, KL Type, Embedded (G), and Extruded Finned Tubes, each have unique characteristics that make them suitable for specific applications.
1. L Type Finned Tubes
- Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers: L Type finned tubes are commonly used in air-cooled heat exchangers where moderate thermal performance is required. The L-shaped fins balance heat transfer efficiency and material cost well.
- HVAC Systems: These tubes are also used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, particularly condenser and evaporator coils.
- Economizers: In power plants, L Type finned tubes are often found in economizers, where they help improve boiler efficiency by preheating the feedwater.
2. LL Type Finned Tubes
- Steam Generators: LL-type finned tubes are used in steam generators, especially in situations where higher thermal performance is required compared to standard L-type tubes. The overlapping fins provide enhanced heat transfer capabilities.
- Waste Heat Recovery Units: LL-type tubes are suitable for waste heat recovery applications where improved thermal efficiency is crucial, particularly in industrial settings.
- Petrochemical Industry: These tubes are used in heat exchangers within petrochemical plants, where they handle high temperatures and corrosive environments.
3. KL Type Finned Tubes
- High-Temperature Heat Exchangers: KL-type finned tubes are designed for applications involving higher temperatures, such as refinery and high-pressure boilers. The knurled fins strengthen the tube’s bond, ensuring better heat transfer efficiency.
- Air Preheaters: In power plants, KL-type finned tubes are used in air preheaters, which help improve the plant’s overall thermal efficiency.
- Refrigeration Systems: These tubes are also found in refrigeration systems that require efficient heat transfer in compact spaces.
4. Embedded (G) Finned Tubes
- Gas Coolers: Embedded (G) finned tubes are ideal for gas coolers, particularly when high thermal efficiency and mechanical strength are required. The fins are embedded into the tube wall, providing excellent heat transfer and durability.
- Furnace Heat Exchangers: These tubes are used in furnace heat exchangers, where they can withstand high temperatures and corrosive environments, making them suitable for industrial heating applications.
- Heat Recovery Steam Generators (HRSG): In HRSG systems, embedded finned tubes contribute to recovering heat from exhaust gases, improving power plants’ overall efficiency.
5. Extruded Finned Tubes
- Chemical Processing Plants: Extruded finned tubes are widely used in chemical processing plants where high thermal efficiency and resistance to corrosion are critical. The extruded fins provide a larger surface area for heat transfer and protect the tube from corrosive substances.
- Air Fin Coolers: These tubes are used in air fin coolers in industries like oil and gas, where they efficiently transfer heat from process fluids to air.
- Condensers and Evaporators: Extruded finned tubes are used in condensers and evaporators in power generation and HVAC systems. Their robust design ensures long-term performance under demanding conditions.



